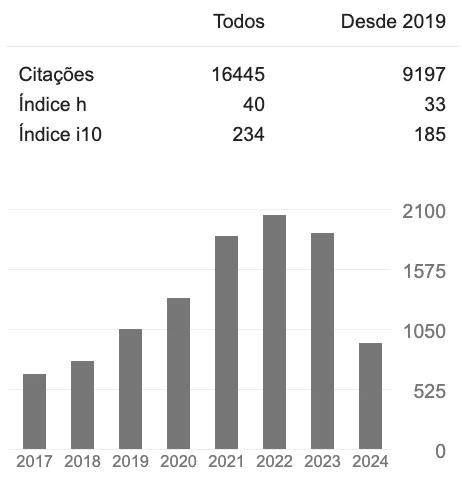
Harvard
Estamos no Dataverse Harvard!
Agora, nossos dados de pesquisa estão acessíveis na prestigiada plataforma Dataverse Harvard. Explore e compartilhe conhecimento conosco. Faça parte dessa rede global de inovação científica!
Seja um Avaliador
Una-se a um grupo seleto de editores e promova o avanço do conhecimento científico.
saiba mais
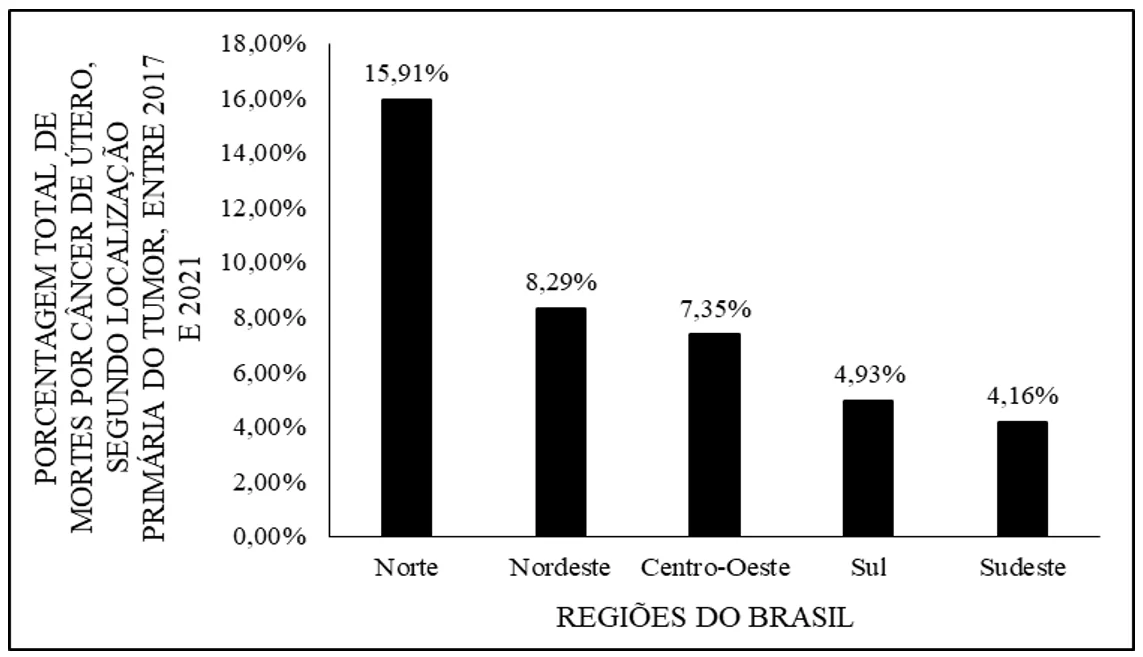
Quantitativo comparado de óbitos por câncer de colo uterino no Brasil e na região norte (Amazônia Brasileira), entre 2017 e 2021
O Câncer de Colo do Útero (CCU) é de extrema relevância, já que possui um número significativo de casos registrados, sendo o terceiro tipo
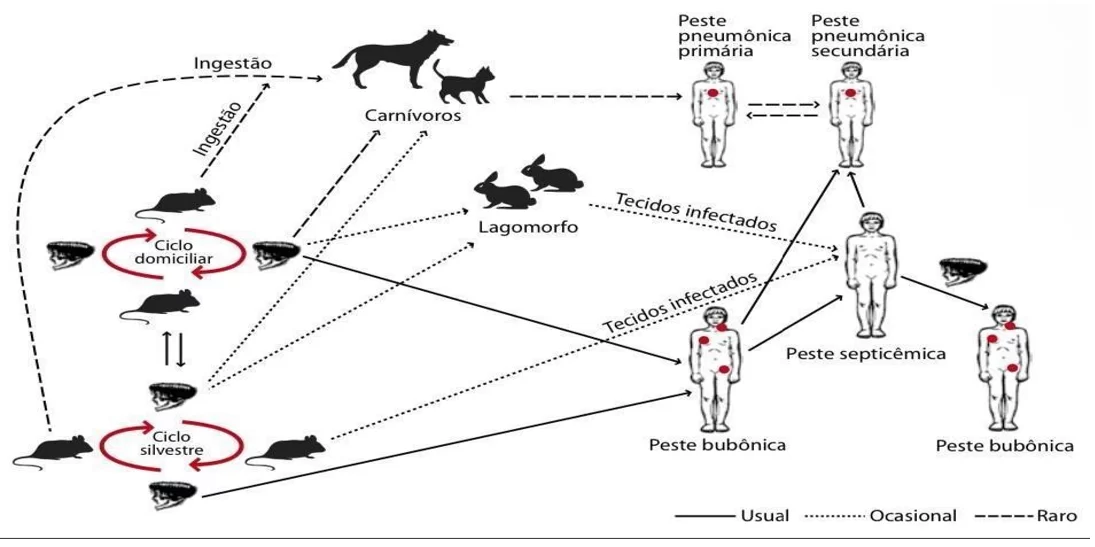
A persistência da peste bubônica em países subdesenvolvidos
A peste bubônica, causada pela bactéria Yersinia pestis, teve um impacto devastador na Europa entre 1347 e 1353, resultando na morte de
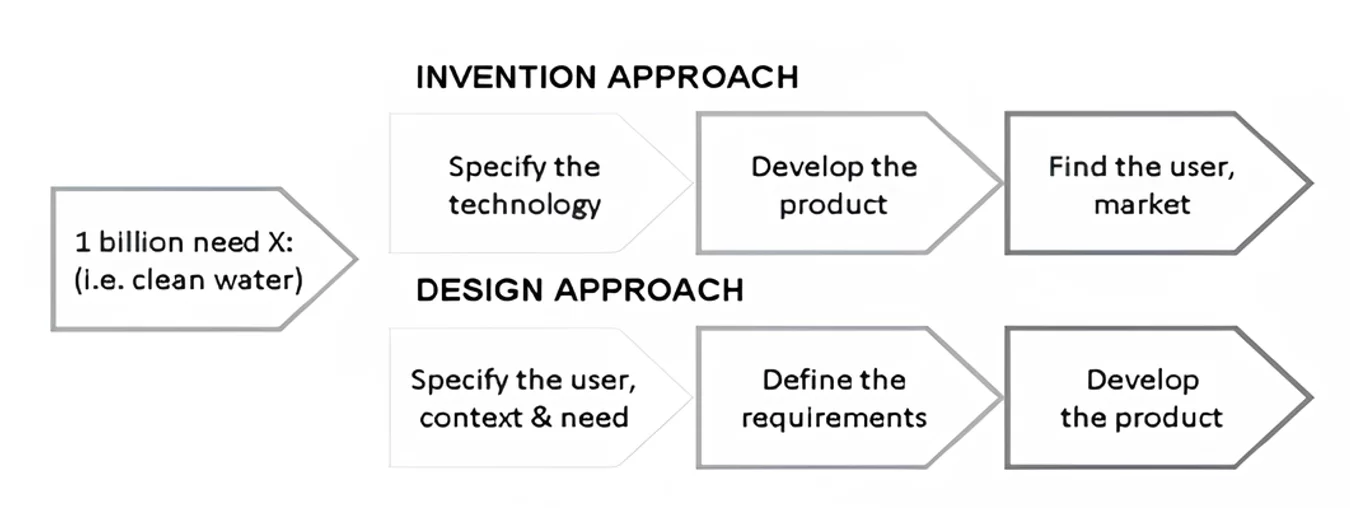
Design centrado no humano aliado aos projetos de inteligência artificial para suporte na área de saúde mental e bem-estar: uma revisão sistemática
Uma em cada oito pessoas apresenta algum tipo de transtorno mental no mundo (WHO, 2022). Os problemas oriundos de uma saúde mental

Desnutrição e perda dentária em idosos: desafios e implicações para a saúde pública
A desnutrição é um fator significativo em idosos que corrobora com a perda dentária e a qualidade de vida. Este estudo revisa a literatura
Internações por acidente vascular cerebral em mulheres, Roraima, Brasil
O Acidente Vascular Cerebral é uma das principais causas de morte e incapacidade globalmente. Mulheres representam mais da metade de todos
Medidas neuroprotetoras e intervenções fisioterapêuticas em recém-nascidos prematuros com hemorragia peri-intraventricular
A Hemorragia Peri-Intraventricular (HPIV) é uma complicação que afeta recém nascidos prematuros, especialmente com idade gestacional
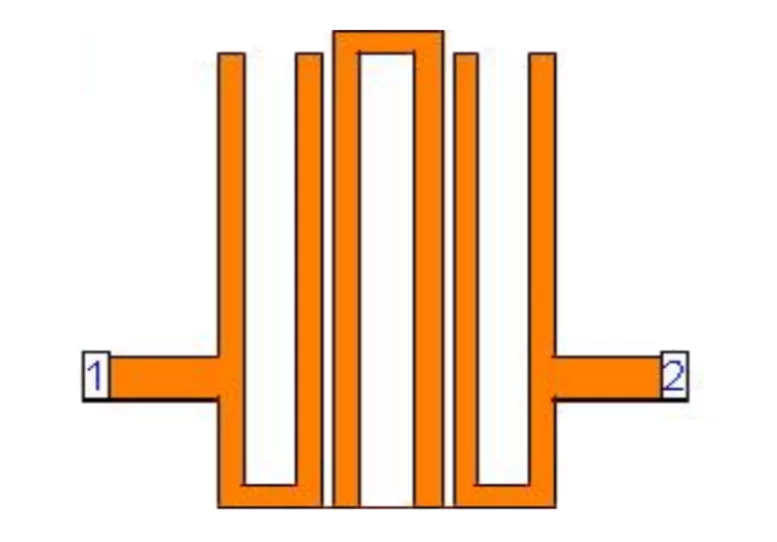
Efeitos geométricos e constitutivos na resposta em frequência de filtros em microstrip lines
Este estudo aborda a influência de variações de características geométricas e constitutivas em filtros de microstrip lines na sua resposta

Criação de sinais-termo para amostra de glossário terminológico de parasitos intestinais humanos em língua brasileira de sinais
A parasitologia é uma área da ciência biomédica que estuda a relação entre o parasito e seus hospedeiros, suas consequências para a saúde
Mediação no tratamento adequado de conflito empresarial familiar
O presente trabalho aborda o entendimento do conflito como elemento natural nas relações humanas, derivados de divergências de interesses

Relações sociais e qualidade de vida: breve análise da produção científica no Brasil
O presente estudo trata da análise da produção científica brasileira em torno do domínio das relações sociais e qualidade de vida. Este
Studygram: uso do Instagram como ferramenta de apoio no estudo da língua coreana
Diante do crescente aumento dos “studygrams” – perfis em redes sociais criados por estudantes que desejam compartilhar suas experiências
Ciências sociais e política: impactos da política nacional de assistência social para o desenvolvimento do Município de Passos
O estudo aborda os impactos da Política Nacional de Assistência Social (PNAS) no município de Passos, MG, destacando seu papel no
Psicanálise, neurociência e linguagem: articulações possíveis
O presente estudo busca estabelecer possíveis articulações entre psicanálise, neurociência e linguagem, considerando suas intersecções
Utilização de Canabidiol no tratamento de crianças com Transtorno do Espectro Autista
O Transtorno do Espectro Autista (TEA) é uma condição neurodesenvolvimental complexa, caracterizada por déficits persistentes na
O impacto do diabetes mellitus no sistema cardiovascular
Introdução: A Diabetes Mellitus é uma doença metabólica e crônica, que tem como característica o alto índice de açúcar (glicose) no sangue
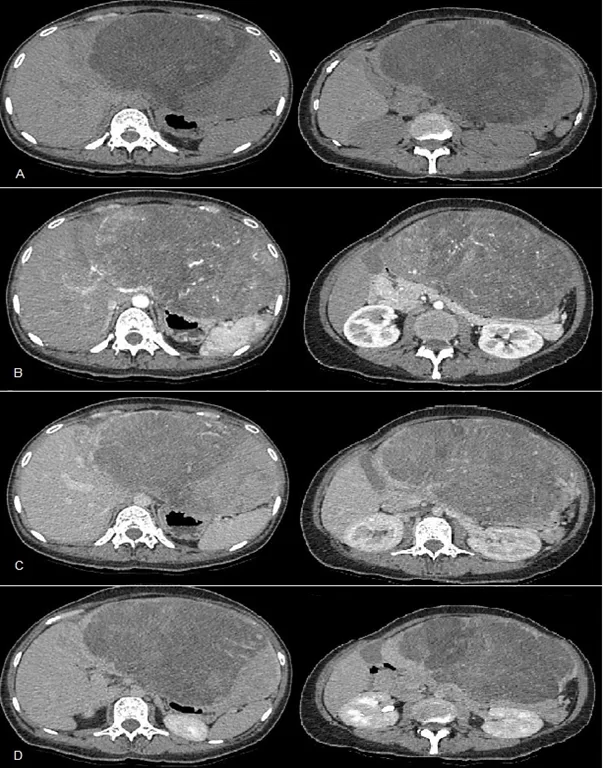
Carcinoma Hepatocelular Atípico: um relato de caso
Objetivo: Relatar um caso de Carcinoma Hepatocelular com apresentação atípica. Relato do caso: Paciente feminina, 30 anos, apresentando
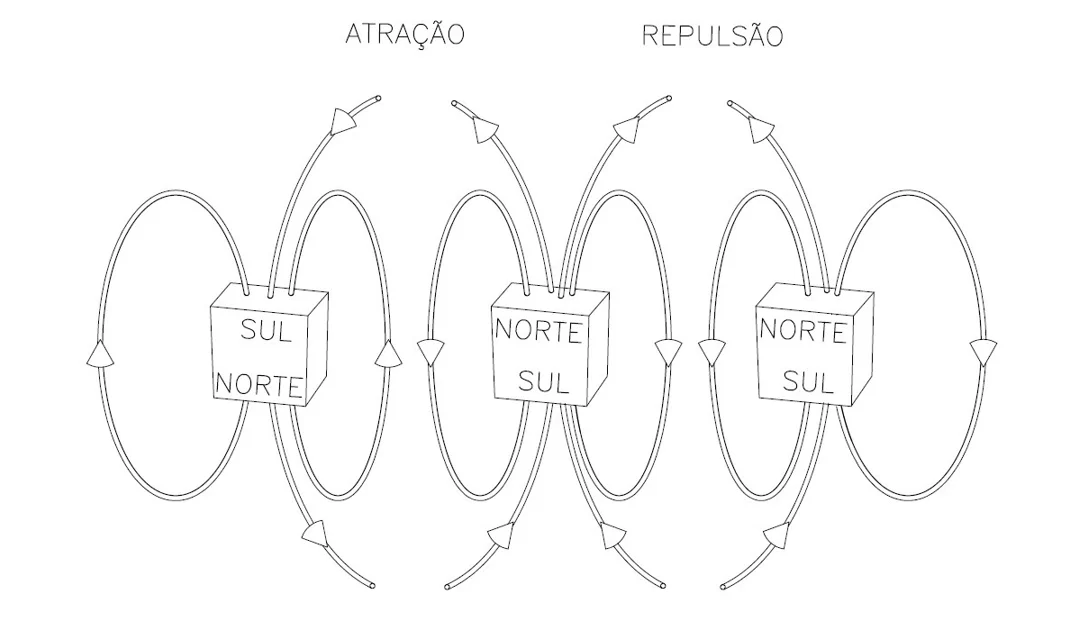
Mudanças no magnetismo e eletromagnetismo, e a criação do motor puramente magnético, chamado moto perpétuo, segundo a TLCG – Teoria das Linhas de Campo Girantes
É apresentado a Teoria das Linhas de Campo Girantes (TLCG), que se baseia em linhas de campo magnético girando em torno de si mesmas, ao
A Gestão da informação direcionada a melhoria da prestação de serviços de uma Organização da Sociedade Civil (OSC) para migrantes
O presente artigo tem por objetivo descrever como o conjunto de práticas decorrentes da GI podem melhorar o atendimento a migrantes em uma
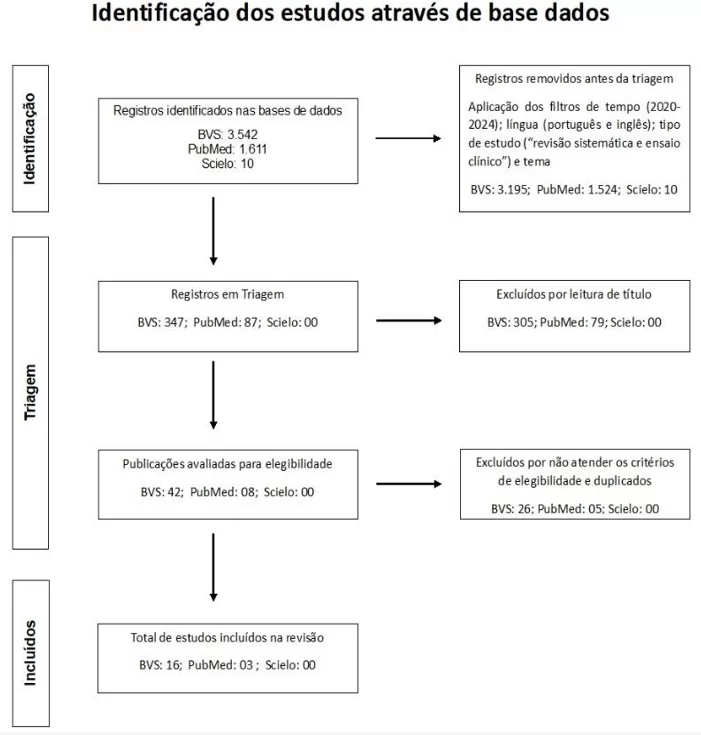
Transtornos psiquiátricos no Covid longa: revisão integrativa da prevalência global
A pandemia de Covid-19 trouxe impactos relevantes e duradouros na saúde mental de grande parte dos indivíduos que tiveram contato com o.
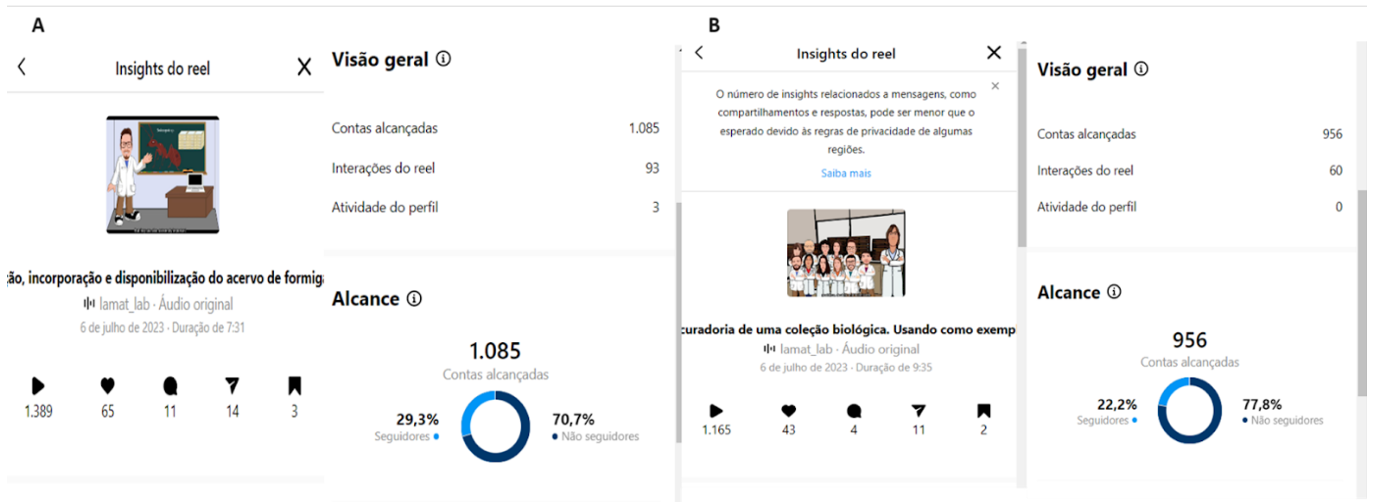
Explorando o impacto do Youtube e Instagram na divulgação científica
Este estudo compara a eficácia de duas plataformas, YouTube e Instagram, na disseminação de conteúdos educativos sobre a recuperação de
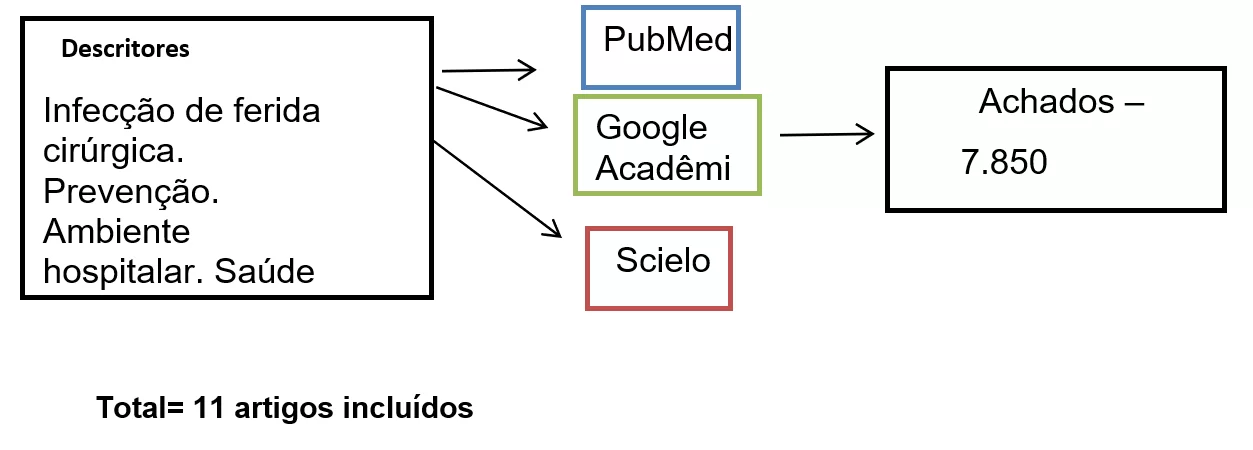
Infecções associadas a feridas cirúrgicas: estudo misto a partir dos fatores de risco e medidas preventivas em ambientes hospitalares
As infecções associadas a feridas cirúrgicas são complicações significativas que podem ocorrer após procedimentos cirúrgicos, impactando
A postura reflexiva do docente de língua inglesa como fator de melhoria da práxis pedagógica
Este artigo trata-se de uma revisão bibliográfica que pretende expor a importância da atitude reflexiva do docente de Língua Inglesa (LI)
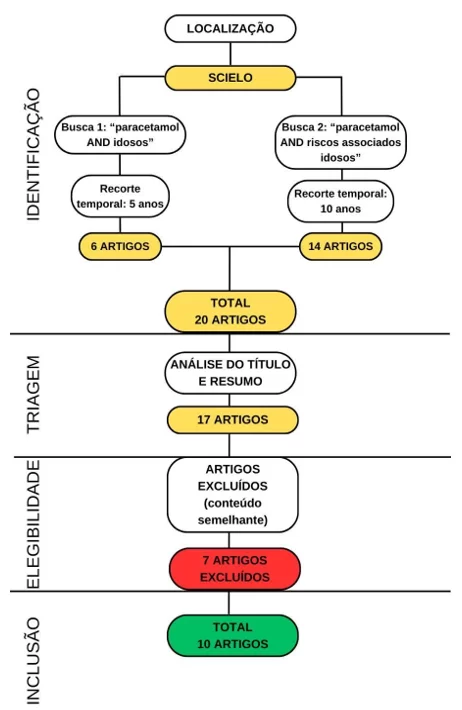
O uso racional do paracetamol e riscos associados na população idosa: revisão integrativa
A automedicação contraria o uso racional e pode apresentar riscos aos pacientes principalmente quando idosos, por exemplo os AINES (Anti
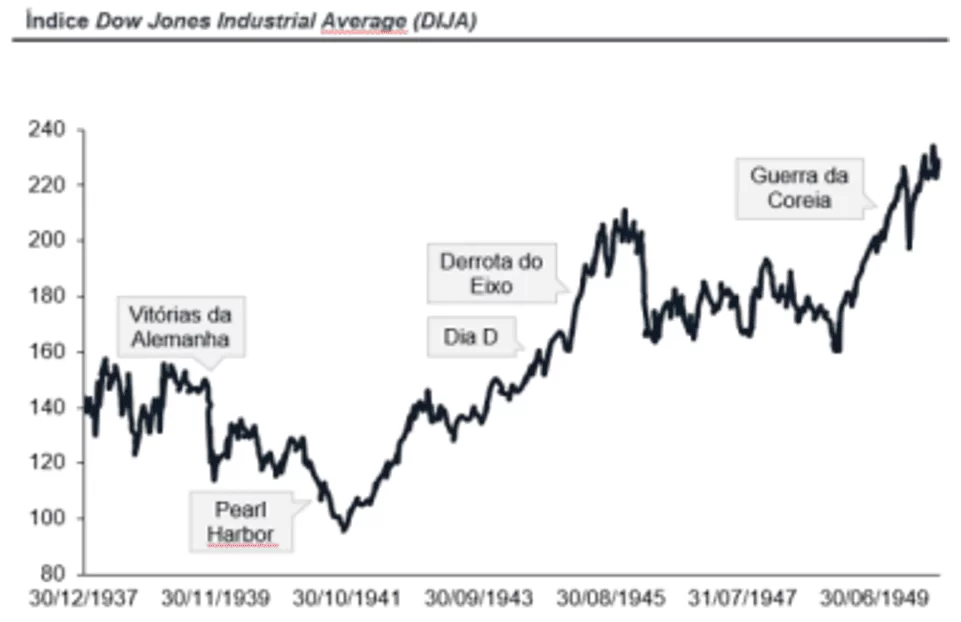
A Segunda Guerra Mundial e as suas repercussões na Administração Contemporânea: transformações históricas, econômicas e organizacionais
O presente artigo visa a exploração do passado como forma de evidenciar os efeitos da tragédia na história mundial nos mundos
Categorias
- Administração
- Administração Naval
- Agronomia
- Arquitetura
- Arte
- Biologia
- Ciência da Computação
- Ciência da Religião
- Ciências Aeronáuticas
- Ciências Sociais
- Comunicação
- Contabilidade
- Design
- Economia
- Educação
- Educação Física
- Engenharia Agrícola
- Engenharia Ambiental
- Engenharia Civil
- Engenharia da Computação
- Engenharia de Produção
- Engenharia Elétrica
- Engenharia Mecânica
- Engenharia Química
- Ética
- Filosofia
- Física
- Gastronomia
- Geografia
- História
- Lei
- Letras
- Literatura
- Marketing
- Matemática
- Meio Ambiente
- Meteorologia
- Nutrição
- Odontologia
- Pedagogia
- Psicologia
- Química
- Saúde
- Sem categoria
- Sociologia
- Tecnologia
- Teologia
- Turismo
- Veterinária
- Zootecnia